Casual Tips About What Are The Disadvantages Of A Closed System

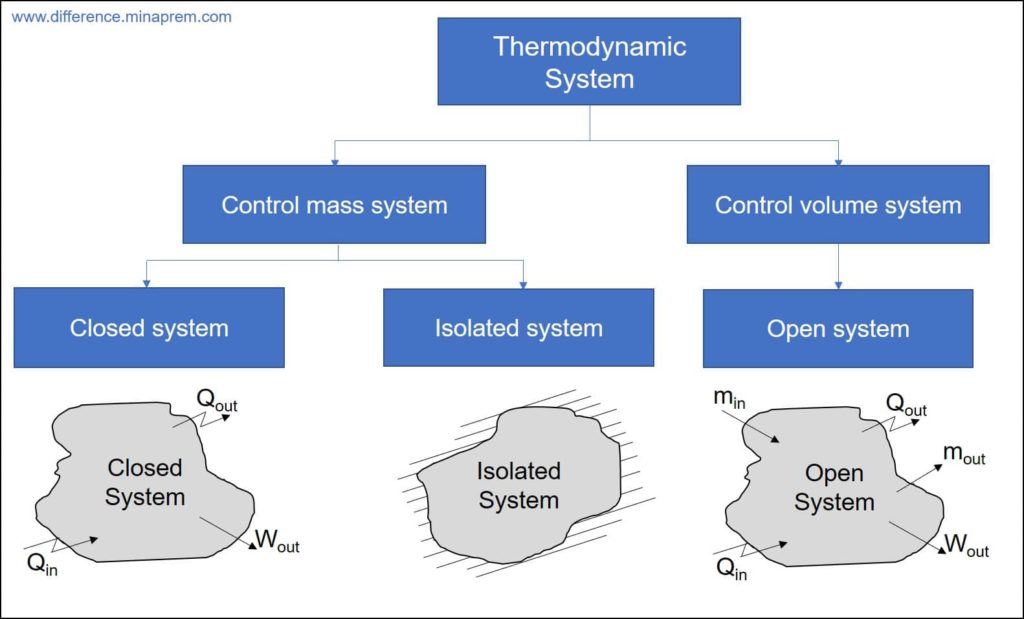
Closed Systems
1. The Allure of Isolation (and Its Downfalls)
Imagine living in a self-contained bubble. No outside influences, no new ideas sneaking in, just the same old stuff circulating endlessly. Sounds peaceful, maybe? But also, a little bit stagnant, right? That's kind of what a closed system is like. In essence, a closed system is one that doesn't exchange matter with its surroundings. Think of a terrarium that's sealed tight, or theoretically, the entire universe (though that one's still up for debate among scientists!). Now, while these systems can be fascinating, there are some real drawbacks to keeping things completely shut off from the outside world. Let's dive into the disadvantages of closed systems to find out more.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of adaptability. When a system is isolated, it can't easily respond to changes in its environment. If a resource becomes scarce or a new threat emerges, the system has limited options for adapting. This can lead to instability and, eventually, failure. A business that refuses to adopt new technologies, for example, might find itself quickly outpaced by its competitors. It is like that old joke "We've always done it this way!" This inflexibility can be a real killer.
Another significant issue is the buildup of waste. In any system, processes generate waste products. In an open system, these waste products can be expelled or recycled. In a closed system, however, waste accumulates over time. This can lead to pollution and toxicity, which can harm the system's components or even cause it to collapse. Think about a sealed aquarium where you never change the water; sooner or later, the fish will start feeling a bit poorly, if you catch my drift. Closed systems can also lead to entropy, which is a fancy way of saying that things tend to get more disordered and chaotic over time. Without fresh energy or resources to counteract this process, the system can slowly degrade.
Finally, the absence of external input limits innovation and creativity. Open systems benefit from the constant flow of new ideas, perspectives, and resources. This allows them to evolve, improve, and adapt to changing circumstances. Closed systems, on the other hand, are stuck with what they have. This can stifle creativity and lead to stagnation. The only "new" ideas are rehashes of the old ones, and its just not the same. A research lab that doesn't collaborate with other institutions might find that its research becomes outdated or irrelevant. In the world of science, collaboration is key; keeping everything under wraps is a recipe for intellectual isolation.

Stagnation Station
2. Why Fresh Air (and Fresh Ideas) Matter
Let's face it, no one thrives in a vacuum. The same holds true for systems, whether we're talking about ecological, economic, or even social ones. When you cut off the flow of fresh information, resources, and perspectives, youre essentially putting the brakes on progress. It's like trying to bake a cake with only the ingredients you had in the pantry last year — things are likely going to be a little stale and maybe a touch moldy! Closed systems are prone to stagnation because they lack the vital inputs needed to adapt, innovate, and grow.
This lack of dynamism can manifest in several ways. For example, imagine a small town that's completely isolated from the outside world. The residents might develop a strong sense of community, but they also run the risk of becoming insular and resistant to new ideas. Their economy might struggle due to a lack of competition and innovation. Their culture might become stagnant and unchanging. Its like living in a time capsule and thats probably not a great thing in the long run.
Furthermore, closed systems can be particularly vulnerable to unexpected shocks. Because they lack the diversity and resilience that come from being open to external influences, they may be unable to cope with sudden changes in their environment. A business that relies solely on a single customer, for example, is at great risk if that customer decides to take their business elsewhere. Similarly, an ecosystem that lacks biodiversity is more susceptible to disease or climate change. In essence, diversity is strength. Just like a well-rounded diet is better for your health than eating only one thing. The same principle applies to entire systems too.
In contrast, open systems tend to be more adaptable, resilient, and innovative. They can draw on a wider range of resources and perspectives to solve problems and seize opportunities. They are also better able to cope with change and uncertainty. A city that welcomes immigrants, for example, is likely to be more dynamic and prosperous than one that is closed off to the outside world. The influx of new ideas, skills, and cultures can spur innovation and create new economic opportunities. The worlds a big, exciting place, so why lock yourself away?

6 Advantages And Disadvantages Of Closed Source Software Drawbacks
The Waste Problem
3. Trash Talk
We've touched upon this already, but it's so critical it deserves its own section. Imagine your house if you never took out the garbage. Pretty soon, it wouldn't be a very nice place to live, would it? Similarly, closed systems face a significant challenge in dealing with waste. Because they don't exchange matter with their surroundings, waste products accumulate over time. This can lead to a variety of problems, from pollution and toxicity to resource depletion and system failure. Think of it as the ultimate hoarder situation but on a much larger scale and with potentially devastating consequences.
In ecological systems, waste accumulation can disrupt natural cycles and harm living organisms. For example, a closed aquarium can quickly become polluted with fish waste and uneaten food. This can deplete oxygen levels, raise ammonia levels, and create a toxic environment for the fish. Similarly, a closed ecosystem that is not properly managed can accumulate pollutants from industrial processes or agricultural runoff. These pollutants can contaminate the soil, water, and air, harming plants, animals, and even humans.
In economic systems, waste accumulation can lead to inefficiency and resource depletion. For example, a factory that doesn't recycle its waste products will eventually run out of raw materials. It will also have to deal with the cost of disposing of its waste, which can be significant. Similarly, a consumer economy that generates excessive waste can deplete natural resources and create environmental problems. Consider all the plastic bottles and packaging that end up in landfills. It's a pretty depressing sight. We really should do better about recycling.
The good news is that there are ways to mitigate the waste problem in closed systems. Recycling is a key strategy. By recycling waste products, we can reduce the amount of new resources that we need to extract from the environment. We can also reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and other disposal sites. Another strategy is to design systems that are more efficient and produce less waste in the first place. This can involve using cleaner technologies, reducing packaging, and promoting sustainable consumption patterns. Ultimately, addressing the waste problem in closed systems requires a combination of technological innovation, policy changes, and individual responsibility.
Innovation Impasse
4. Thinking Outside the Box (Because There Is No Box!)
Ever tried brainstorming ideas with the same group of people day after day? It can feel like youre just going in circles, rehashing the same old thoughts. That's a perfect example of the limitations of a closed system when it comes to innovation. Without external input, creativity tends to stagnate. Closed systems lack the diversity of perspectives, resources, and ideas needed to generate truly novel solutions. Its like trying to write a symphony with only a handful of notes — youll get something, but it probably wont be very inspiring!
In scientific research, for instance, a lab that isolates itself from other institutions might miss out on important breakthroughs. Collaboration and open communication are essential for advancing knowledge. Researchers need to share their findings, exchange ideas, and learn from each other. Similarly, a business that doesn't seek out customer feedback or monitor its competitors is likely to fall behind. Its important to know what the rest of the world is doing.
Even in artistic endeavors, isolation can be detrimental. Artists often draw inspiration from their surroundings, from other artists, and from different cultures. By limiting their exposure to new experiences, they risk becoming creatively stale. Think of a musician who only listens to one genre of music, for example. They're unlikely to develop a very original sound. Its important to have exposure to different cultures, opinions, and so on to keep fresh!
The key to fostering innovation is to create systems that are open to external influences. This can involve promoting collaboration, encouraging diversity, and embracing change. It also means being willing to challenge assumptions and experiment with new ideas. A company that actively seeks out feedback from its customers, partners with other businesses, and invests in research and development is more likely to be innovative than one that remains closed off. The best ideas often come from unexpected places, so its important to keep an open mind and be willing to explore new possibilities.
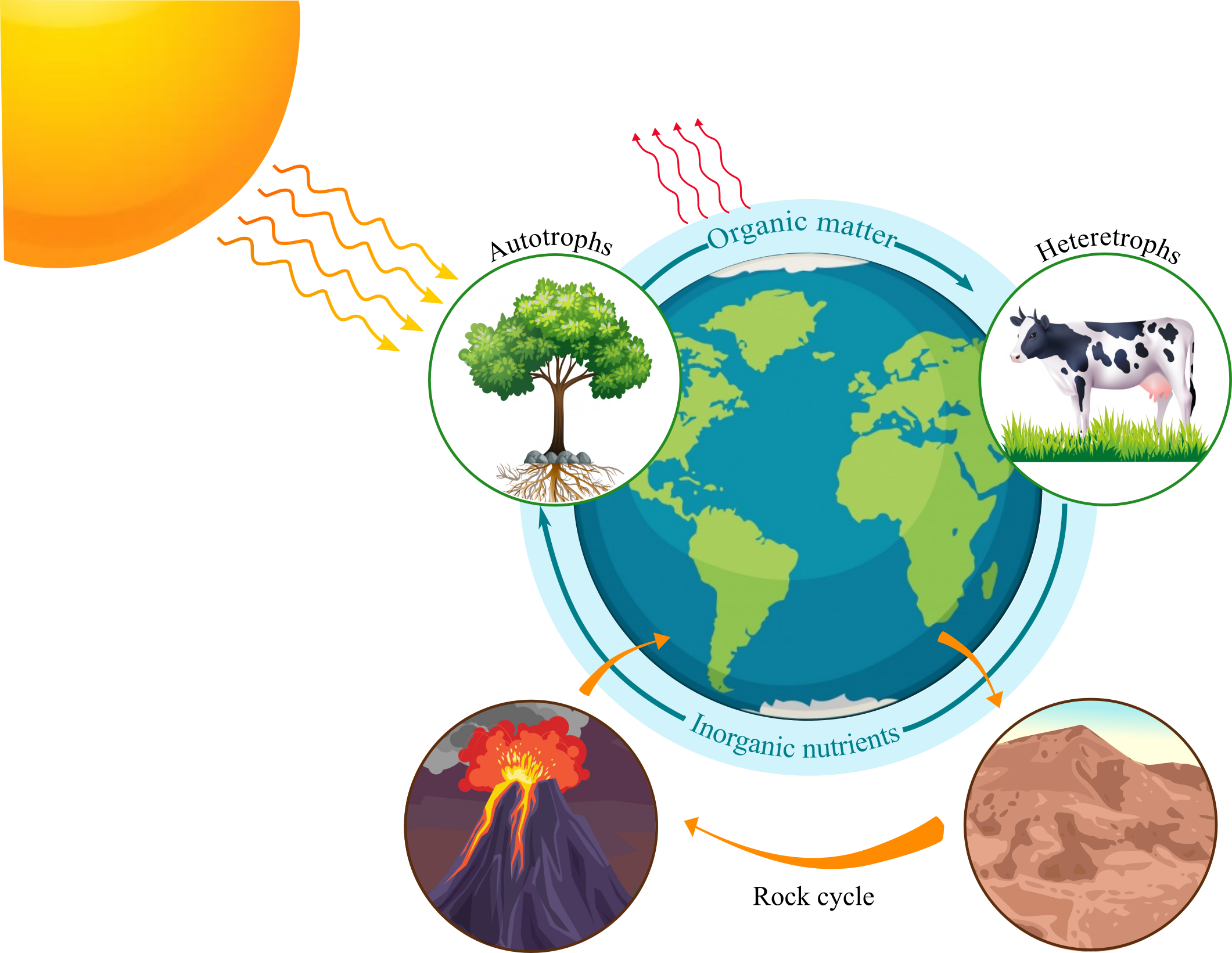
Earth As An Open And A Closed System
Beyond the Bubble
5. Exceptions to the Rule
Okay, so we've spent a lot of time bashing closed systems. But, to be fair, there are a few situations where a closed approach might actually be beneficial, or at least, less detrimental. These are typically situations where control, security, or simplicity are paramount. Think of a highly secure data center, for example. It's likely to be physically and digitally isolated from the outside world to protect sensitive information. In this case, the benefits of security outweigh the potential drawbacks of limited innovation.
Another example might be a spacecraft on a long-duration mission. While not completely closed (they do receive solar energy), spacecraft aim to recycle as much as possible and minimize the exchange of matter with their surroundings. This is essential for survival in a harsh environment where resources are scarce. Every gram of water or oxygen counts, so recycling is key. The crew cant simply open a window and let in some fresh air.
Similarly, in certain manufacturing processes, a closed system might be used to ensure purity or prevent contamination. For example, a pharmaceutical company might use a closed system to produce sterile medications. This helps to minimize the risk of introducing harmful bacteria or viruses into the product. Think of medical grade systems, to avoid infections and so on.
However, even in these cases, it's important to be aware of the potential downsides of a closed system. It's also important to implement strategies to mitigate these downsides. For example, even a highly secure data center should still have some form of external monitoring to detect potential threats. And even a spacecraft should have backup systems in place to deal with unexpected emergencies. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to use a closed system depends on the specific context and the tradeoffs involved. It's not a one-size-fits-all solution, and it's important to weigh the pros and cons carefully.